Advanced Skin Cancer Detection Using CNN and Transfer Learning
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr491Keywords:
Dermoscopic images, Deep learning, Convolutional neural networks, Skin cancer diagnosis, Transfer learningAbstract
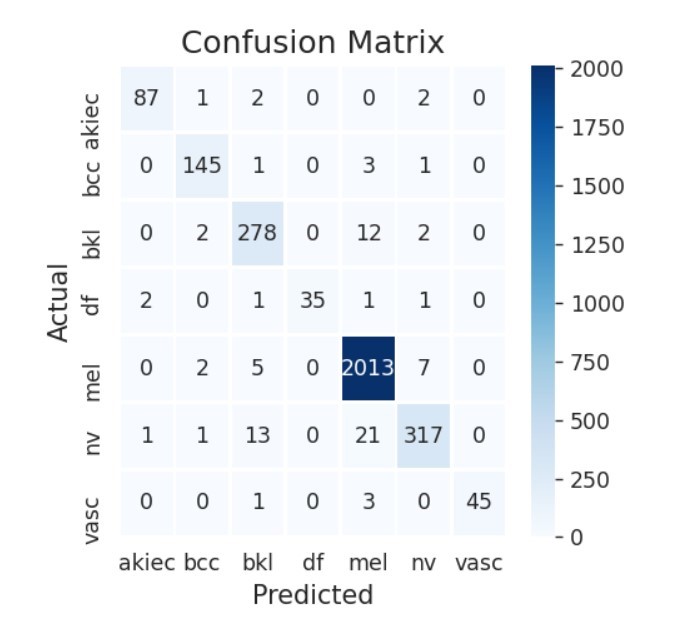
Because skin cancer can appear right away and may spread fast, it is considered one of the most dangerous types of cancer. When cells begin dividing faster than normal, they build up in one area, invade other tissue and move to several parts of the body. Finding cancer early allows doctors to control it before it becomes serious and requires more intensive treatments. Thanks to CNNs, skin cancer diagnosis now relies on finding in-depth details in images, allowing lesions to be classified with accuracy. Through early detection, they help dermatologists spot skin changes at their earliest point which is valuable for patient health. This research introduces a novel use of CNN for the task of classifying skin cancer lesions. This study tests the CNN model using the unbalanced datasets: HAM10000. Other transfer learning models used in this paper are Xcepton, and DenseNet201 and they are evaluated alongside the CNN model. Forecasts are measured using four main evaluation metrics: accuracy, recall, precision, F1-score, specificity and. Results from the experiments reveal that the proposed CNN model does better than other deep learning (DL) models that used these datasets. The proposed model delivered the best results on HAM10000 (97:4%). The results prove that using CNN as a model helps solve problems related to class imbalance and leads to greater accuracy in detecting skin cancer. Moreover, the model suggested here outperforms other recent studies that use the same data, particularly in accuracy, indicating that the CNN is robust and effective.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Hira javaid, Muhammad Kamran Abid, Muhammad Hamza Saleem, Saima Ali Batool, Muhammad Fuzail, Ahmad Naeem, Naeem Aslam (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






