ENHANCING CLINICAL APPLICABILITY OF CNN MODELS FOR PNEUMONIA DETECTION IN CHEST X-RAYS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr770Keywords:
Pneumonia diagnosis, Clinical usability of diagnostic tools, Improving healthcare outcomes, Medical imaging (Chest X-ray analysis)Abstract
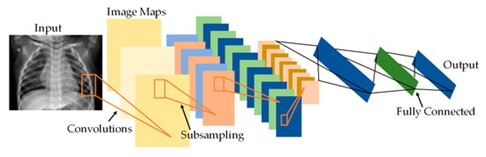
In order to lower the mortality rates linked to pneumonia which continues to be a major danger to global health quick and precise diagnostic tools are required. Deep learning combined with chest X-ray imaging has become a revolutionary method for automatic pneumonia identification. By carefully assessing and refining four well-known architectures AlexNet, ResNet18, DenseNet201 and SqueezeNet this study aims to improve the clinical usability of convolutional neural network models. In order to replicate real-world clinical limitations, we used transfer learning and trained each model only on CPU-based hardware using a three-class chest X-ray dataset of 5,863 pictures classified into normal, bacterial pneumonia and viral pneumonia. Classification accuracy computing efficiency and deployment feasibility in resource-constrained environments were used to evaluate performance. Our results show that while all models achieve impressive accuracy ResNet18 and DenseNet201 are especially well-suited for real-world clinical implementation without requiring expensive GPU infrastructure because they strike the ideal balance between diagnostic precision and computational feasibility. In order to enable efficient and trustworthy pneumonia detection in a variety of healthcare settings this study offers a useful and comparative approach for CNN model selection and optimization.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sabeen Fatima Majid, Dr. Hira Zahid, Nabeeha Sahar, Hamza Khan, Shahzad Nasim (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






