ROLE OF SONOGRAPHY IN THE EVALUATION & MANAGEMENT OF NEONATAL JAUNDICE: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr527Keywords:
Neonatal jaundice, sonography, biliary atresia, shear-wave elastography, gallbladder abnormalities, MV-flow imaging, neonatal liver, diagnostic ultrasoundAbstract
Background: Neonatal jaundice is a widespread condition affecting a significant proportion of newborns. While often benign, it may indicate underlying hepatobiliary or neurological pathology, necessitating prompt diagnosis. Sonography, as a non-invasive imaging tool, has gained prominence in neonatal settings.
Objectives: This systematic review aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and clinical utility of various sonographic modalities—including grayscale ultrasound, Doppler, shear-wave elastography (SWE), and cranial microvascular flow (MV-Flow) imaging—in the evaluation and management of neonatal jaundice.
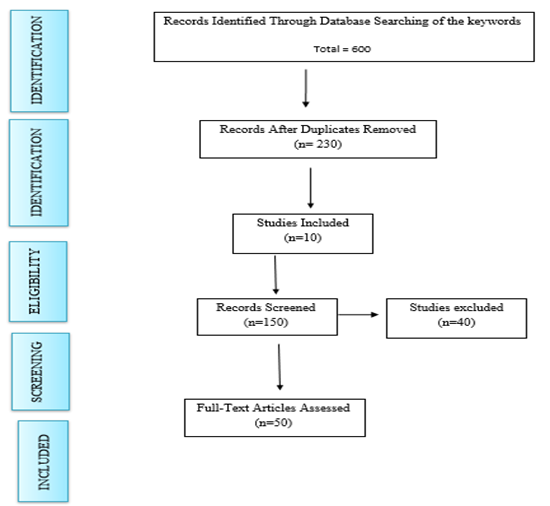
Methods: Following PRISMA guidelines, a literature search was conducted using PubMed, Google Scholar, and Springer for original studies published between 2015 and 2025. Ten studies met the inclusion criteria and were analyzed for study design, population, sonographic findings, and diagnostic accuracy.
Results: Across the included studies, sonographic techniques demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity in detecting biliary atresia, liver abnormalities, and gallbladder anomalies. SWE provided quantifiable liver stiffness measurements, aiding differentiation between transient and obstructive jaundice. The use of MV-Flow imaging in cranial sonography offered novel insights into bilirubin-induced brain injury. Sensitivity values reached up to 100% in some models, with specificities frequently exceeding 90%.
Conclusion: Sonography is a highly effective diagnostic modality for neonatal jaundice, particularly when enhanced with advanced imaging techniques. Standardization of protocols, expanded use of SWE and MV-Flow, and integration of AI tools are recommended to further improve diagnostic precision and clinical outcomes.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Ibrahim Khan, Syed Zaigham Ali Shah, Shujaat Hussain, Amir Nawaz (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






