ADVANCING NAMED ENTITY RECOGNITION FOR URDU: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MACHINE LEARNING AND DEEP LEARNING APPROACHES
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr536Keywords:
Urdu Named Entity Recognition (NER), Machine Learning, Deep Learning, BiLSTM-GRU, mBERT, XLM-RoBERTa, Conditional Random Field (CRF), Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Sequence Labeling, Low-Resource Languages, Natural Language Processing (NLP), Text Classification, Urdu Language ProcessingAbstract
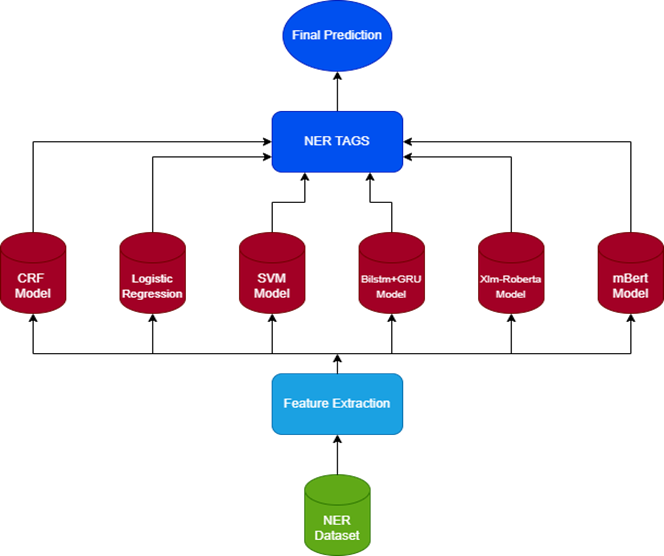
This paper introduces both Machine Learning (ML) and state-of-the-art Deep Learning (DL) methods for Named Entity Recognition (NER) in Urdu a low-resource language. The work compares a variety of models such as Conditional Random Fields (CRF), Logistic Regression, Support Vector Machines (SVM), BiLSTM+GRU, mBERT, and XLM-RoBERTa on a cross domain dataset of more than 1 million tokens for eight entity classes. Performance was compared using typical metrics: precision, recall, F1-score, and accuracy. Among the ML models, CRF had the best F1-score of 0.9899 and accuracy of 97%, lagging behind Logistic Regression and SVM. However, deep learning models performed much better than traditional approaches. The results show that our proposed hybrid technique outperforms existing state of the art techniques on Urdu NER, achieving an F-score of up to 0.997 when using BiLSTM+GRU, followed closely by XLM-RoBERTa and mBERT with F1-scores of 0.9969 and 0.996, respectively. One of the novel contributions of this paper is training and testing models on naturally ordered, domain-specific Urdu text, and building an in-house annotated corpus. It is proven from our results that transformer-based and hybrid recurrent models perform incredibly well for under-resourced NER tasks given the provision of clean, domain-specific data. This paper opens the way to future work on building real-world NLP applications for under-resourced languages.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Ali Hassan, Talha Farooq Khan, Mubasher Malik, Muhammad Sabir, Abdul Haseeb Qureshi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






