COMPARATIVE ULTRASOUND ASSESSMENT OF RENAL PARENCHYMAL THICKNESS AND RENAL FUNCTION TESTS IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr241Keywords:
CKD, eGFR, serum creatinine, renal parenchymal thickness, ultrasonographyAbstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a global public health problem with increasing incidence, poor prognosis, and significant economic burden. Early detection and monitoring are crucial in mitigating adverse outcomes. Ultrasonography is a non-invasive, cost-effective tool for evaluating renal function, particularly renal parenchymal thickness, in CKD patients.
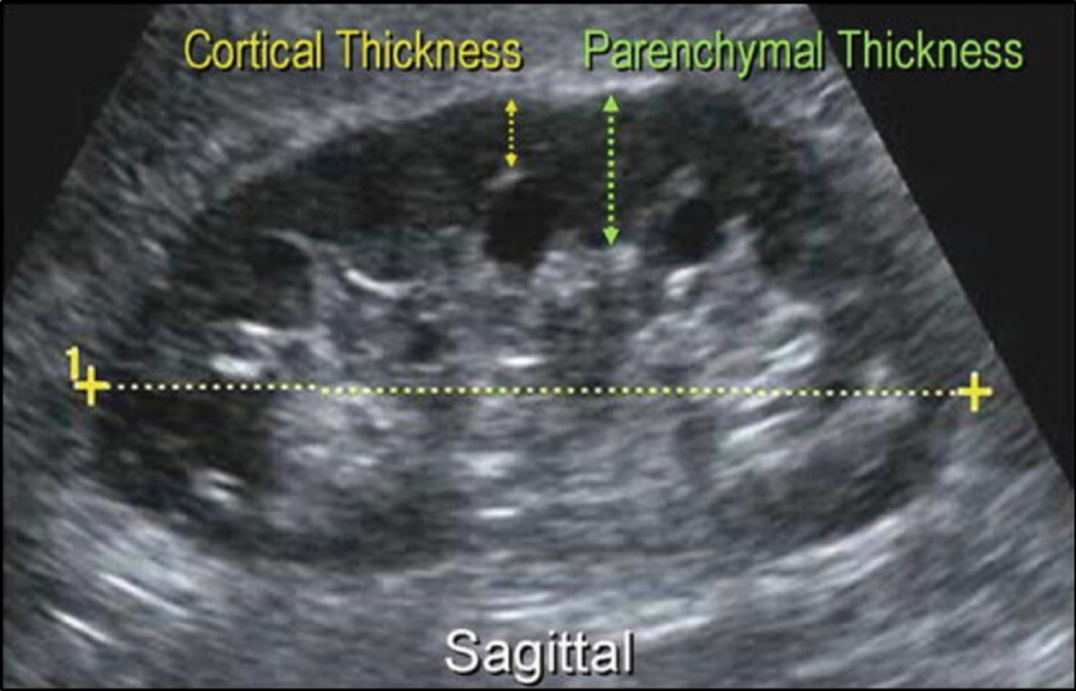
Objective: To compare renal parenchymal thickness using ultrasound findings between CKD patients and healthy controls, and to evaluate differences in renal function tests (RFTs) between these two groups.
Methods: This case-control study involved 64 CKD patients and 64 healthy controls. Renal parenchymal thickness was measured via ultrasound, while serum creatinine levels and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) were assessed as part of the RFTs. Statistical analyses were performed to compare these parameters between the groups.
Results: CKD patients exhibited significantly lower mean parenchymal thickness (8.51 ± 3.03 mm) compared to controls (15.82 ± 1.78 mm, p < 0.001). Serum creatinine was significantly elevated in CKD patients (9.05 ± 5.14 mg/dL) compared to controls (1.05 ± 0.25 mg/dL, p < 0.001). Similarly, eGFR was markedly reduced in CKD patients (14.01 ± 15.04 mL/min/1.73m²) relative to controls (106.56 ± 7.92 mL/min/1.73m², p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Renal parenchymal thickness, serum creatinine, and eGFR are significant and independent predictors of CKD progression. Ultrasonography is a reliable, non-invasive diagnostic tool for assessing structural renal changes in CKD.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Waqas Ahmad, Hifsa Mobeen, Arsalan Waqas Ahmad Shah, Naima Mobeen, Asad ur Rehman, Asma Bibi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






