OPTIMIZING LEAD-FREE CsGeI3 PEROVSKITE SOLAR CELLS: SCAPS-1D SIMULATION ACHIEVING 27.34% EFFICIENCY THROUGH LAYER THICKNESS AND BAND ALIGNMENT TUNING
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr632Keywords:
Perovskite Solar cell, CsGeI3, Numerical Simulation, SCAPS 1-D, Inorganic Perovskite, Lead-free Perovskites, TiO2 ETL, CuSCN HTLAbstract
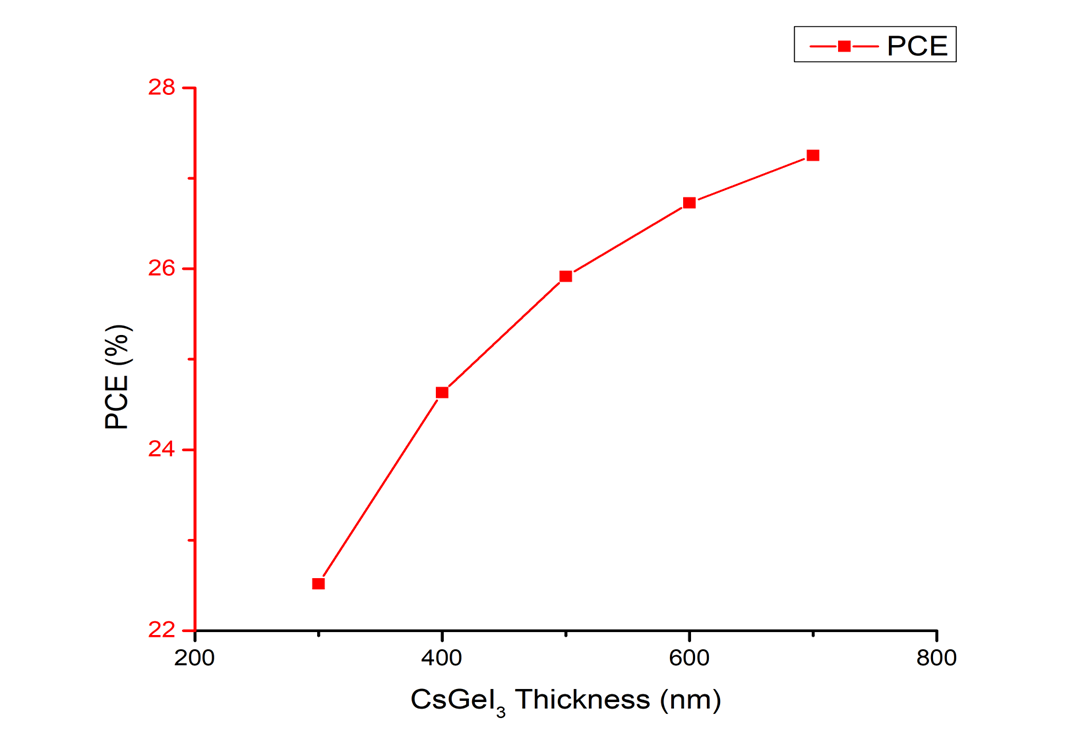
Lead-free perovskite solar cells (PSCs) present a sustainable alternative to conventional lead-based devices by mitigating toxicity concerns. In this work, we use SCAPS-1D numerical simulations to optimize an all-inorganic CsGeI3-based PSC structure incorporating TiO2 as the ETL and CuSCN as the HTL. The study systematically explores the influence of absorber thickness (300-700 nm), ETL thickness (50-250 nm), HTL thickness (100-500 nm), and the electron affinities of each layer (CsGeI3; 3.9-4.1 eV; TiO2: 4.18-4.34 eV; CuSCN: 1.6-1.8 eV) on device performance. Key photovoltaic parameters VOC, JSC, FF, and PCE are analyzed under these variations. The optimized device achieves a PCE of 27.34%, with VOC ≈ 1.33 V, JSC ≈ 23.59 mAcm-2, and FF ≈ 86.89%. These enhancements are attributed to efficient charge carrier generation, reduced recombination, and favorable band alignment. The external quantum efficiency approaches 100% across the 390-700 nm wavelength range, indicating strong visible-light absorption. Overall, the results demonstrate the high potential of CsGeI3 for environmentally friendly, high-performance PSCs and provide valuable design guidelines to support experimental realization in renewable energy applications.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Yasir Nawaz Khan, Azhar Nawaz, Ayaz Husnain (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






