DEVELOPMENT OF HIGH YIELDING DOUBLE CROSS MAIZE HYBRIDS USING 9 X 9 DIALLEL METHOD
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr232Keywords:
Combining ability, Heterosis study, Gene action, Heritability, Inbreeding depressionAbstract
Diallel analysis is one of the methods to develop and evaluate F1 and F2 hybrid crosses for desirable parameters based on mode of gene actions. The experiment entitled “Development of high yielding double cross F1 maize hybrids utilizing 9 x 9 full diallel method” was selected and conducted at Bacha Khan University Agriculture Research Farm during Kharif season 2021-22.Eight F1 Maize hybrids and one open pollinated variety of sweet corn were crossed in all possible combinations and produced 72 double crosses F1 hybrids including reciprocals and compared with 9 parents. Experiment was laid out in a partial lattice square design with 9 blocks having 9 entries each with three replications. After analyzing the data on the following parameters: Days to 50% Anthesis, Days to 50% Silking, Days to 50% Anthesis Silking Interval (ASI), Height of Cob, Plant Height and Grain Yield; significant differences were observed among the double cross F1 hybrids for almost all of the parameters with the exception of the parameters: Number of cobs, Plant height, cob diameter and cob length. The traits having significant results were further subjected to genetic analysis for finding mode of gene actions, genetic components of variation and heritabilities of significant parameters. Highly significant variations were observed for all genetic components using Hayman’s approach regarding grain yield, which indicated presence of additive (A), dominance (B), directional dominant (B1), non-symmetrical genes distribution. Significant values of maternal (C) and reciprocal effects (D) for all parameters indicated retesting of A and B effects to make them non-significate for having no maternal and reciprocal effects.
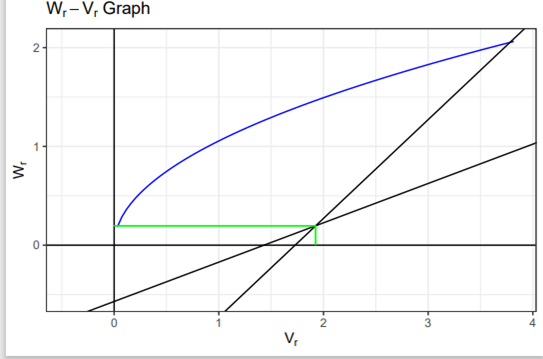
The Wr-Vr graph showed that the regression line cuts the y-axis above the origin for all parameters. This is an indication that partial dominance type of gene action is controlling the traits under study.
The value for broad sense heritability was larger than narrow sense heritability for parameters: (days to 50% tasseling, days to anthesis, days to silking, ASI and grain yield). This indicated that main role was played by non-additive genes in the expression of these parameters.
Component of variation for days to 50% tasseling, days to silking and height of cob, pointed out that GCA variance was greater than SCA variance indicating the importance of additive gene effects for the control of the trait. While, Components of variance for ASI, days to 50% anthesis and grain yield indicated that SCA variance was greater in magnitude than GCA variance giving a greater estimate of variance due to dominant effects. Minimum Days to 50% Anthesis was noted for 6 x 5 (55 days), whereas minimum days to 50% tasseling was observed for 9 x 2, 1 x 5 and 1 x 10 (54 days). Minimum ASI was noted for 2 x 4, 6 x 6, 5 x 8, 4 x 1, 5 x 9, 5 x 2, 7 x 6, 7 x 10 (3 days). F1 (1 x 4, 1 x 7, 1 x 8, 1 x 10, 2 x 1, 2 x 5, 2 x 6, 4 x 10, 6 x 2, 6 x 8, 6 x 7, 6 x 10, 7 x 1, 7 x 5, 7 x 10, 8 x 7, 8 x 9, 8 x 10, 9 x 1, 9 x 2, 9 x 6, 9 x 7, 10 x 1) gave maximum grain yield. Further suggested that the above mentioned crosses should be utilizing in the coming breeding programs for more desire improvement from all angles (qualitative and quantitative).
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mansoor Ali Shah, Dr Syed Salim Shah, Kashif Zafar, Zahid Iqbal, Inzimam Ul Haq, Muhammad Arif (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






