SYNTHESIS OF ZNO NANOPARTICLES USING ALOE VERA GREEN SOURCE AND THEIR ANTIBACTERIAL PROPERTIES
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr343Keywords:
Green synthesis, ZnO nanoparticles, Aloe vera, antibacterial activity, reactive oxygen species, sustainable nanotechnologyAbstract
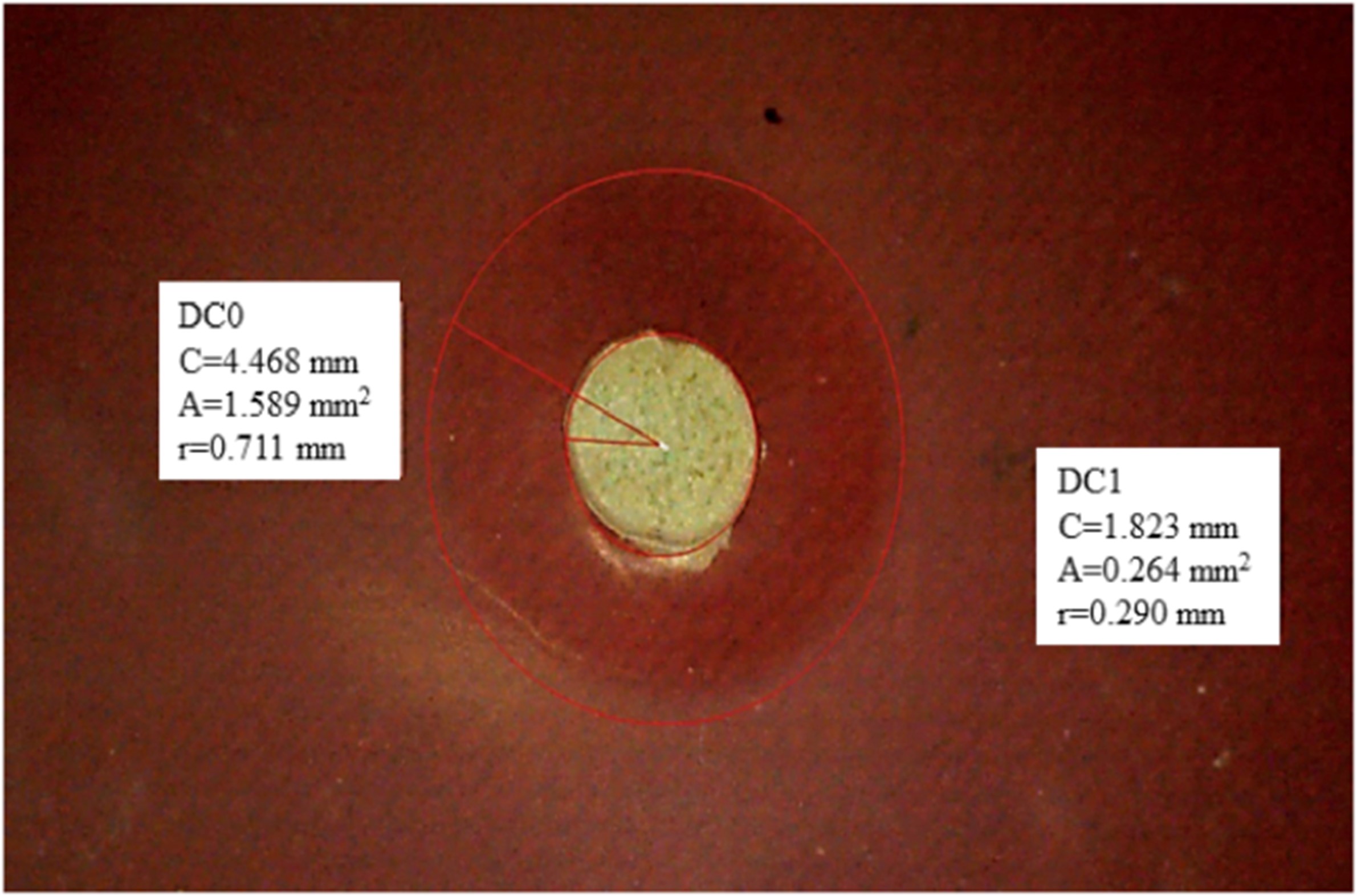
The green synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) has gained significant attention due to its eco-friendly, cost-effective, and non-toxic approach. This study synthesizes ZnO NPs using Aloe vera extract as a natural reducing and stabilizing agent. The bioactive compounds in Aloe vera facilitate nanoparticle formation, eliminating the need for hazardous chemicals. The synthesized ZnO NPs were characterized using UV-Vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) to confirm their structural, morphological, and elemental properties. The antibacterial potential of ZnO NPs was evaluated against Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli) bacterial strains using the agar well diffusion method. The results revealed significant antibacterial activity, with ZnO NPs exhibiting larger zones of inhibition compared to control samples. The mechanism of action was attributed to reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, bacterial membrane disruption, and metal ion release, leading to cell damage and death. This study highlights the potential of Aloe vera-mediated ZnO NPs as an efficient antimicrobial agent with promising applications in biomedicine, food preservation, and agriculture. The eco-friendly synthesis method aligns with sustainable nanotechnology goals, reducing environmental toxicity while maintaining high bioactivity. Further research on optimizing synthesis parameters and evaluating long-term stability can enhance the practical applicability of these nanoparticles.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Awais Ur Rehman, Aysha Nisar, Rabia Iftikhar, Muhammad Shahzaib Hassan, Benish Saeed, Muniba Fatima, Shah Wali Ullah, Waqar Ul Hassan, Waqas Mahmood (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






