CITRIC ACID MEDIATED GREEN SYNTHESIS OF COPPER NANOPARTICLES USING CINNAMON BARK EXTRACT: STRUCTURAL CHARACTERIZATION, CATALYTIC EFFICIENCY, AND ANTIBACTERIAL APPLICATIONS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr643Keywords:
Copper nanoparticles (CuNPs), Green synthesis, Cinnamon bark extract, Citric acid mediation, Nanoparticle characterization, Antibacterial activityAbstract
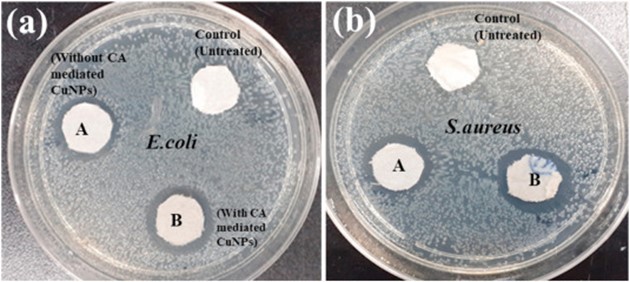
The synthesis of copper nanoparticles (CuNPs) through eco-friendly methods has attracted significant attention as a sustainable alternative to conventional chemical approaches that rely on hazardous reagents. In this study, a novel citric acid-mediated biosynthetic route was developed using cinnamon bark extract as both a reducing and stabilizing agent. Citric acid played a dual role in enhancing the reductive capability of cinnamon phytochemicals and in controlling nanoparticle morphology, resulting in highly stable, spherical CuNPs with uniform surface roughness. The synthesized nanoparticles were characterized using UV–Vis spectroscopy, SEM, XRD, and FTIR analyses, which confirmed their crystalline structure, homogeneous distribution, and biomolecule-assisted capping. Functional assessment demonstrated remarkable catalytic efficiency, with CuNPs achieving over 80% degradation of the carcinogenic dyes methylene blue (MB) and methyl orange (MO) in the presence of sodium hypophosphite, a non-toxic reducing agent. Furthermore, antibacterial studies against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli revealed superior inhibition zones, particularly in citric acid-assisted CuNPs, underscoring their broad-spectrum antimicrobial potential. The combined catalytic and antibacterial properties highlight the versatility of these nanoparticles for environmental and biomedical applications. This green synthesis route not only eliminates the use of toxic chemicals but also offers a cost-effective and scalable strategy for producing CuNPs suitable for wastewater remediation, medical fabrics, and personal protective equipment, contributing to sustainable nanotechnology advancements.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Abdul Qadeer, Muhammad Fahad Hayat, M Lateef, Muhammad Sheeraz, Muhammad Aqib Majeed, Muhammad Shahbaz (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






