PROBING STRUCTURAL AND FUNCTIONAL GROUP FEATURES OF NICKEL OXIDE TOWARD IMPROVED DRUG LOADING EFFICIENCY
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr596Keywords:
Nickel oxide, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, Co-precipitation, Nanocarriers, Drug loadingAbstract
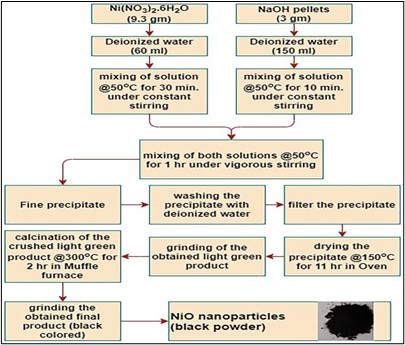
Nanotechnology has emerged as a transformative field in biomedical science, providing innovative approaches for disease detection, diagnosis, and therapy through the design of functional nanomaterials that interact precisely with biological systems. Among the various nanomaterials, nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles have attracted considerable attention due to their excellent chemical stability, affordability, and versatile physicochemical properties, which make them promising candidates for applications ranging from drug delivery to imaging and therapeutic platforms. In this study, NiO nanoparticles were synthesized using a simple, reproducible, and cost-effective chemical co-precipitation method, chosen for its scalability and suitability for large-scale production. The prepared NiO nanoparticles were subjected to Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) to investigate their structural features and identify functional groups present on their surface, as these characteristics play a decisive role in drug–nanoparticle interactions. The outcome of this study provides a foundation for the rational design of NiO-based nanocarriers and highlights the importance of further investigations into particle size control, surface functionalization strategies, and biocompatibility assessments to optimize their performance for advanced drug delivery systems and clinical applications.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Talha Naseer, Shehr Bano, Kanwal Akhtar, Ayesha Younus, Yasir Javed, Umbar Zulfiqar (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






