ECO-FRIENDLY SYNTHESIS OF SILVER NANOPARTICLES FROM POMEGRANATE PEEL EXTRACT AND THEIR ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr383Keywords:
Green synthesis, Silver nanoparticles, Pomegranate peel extract, Antibacterial activityAbstract
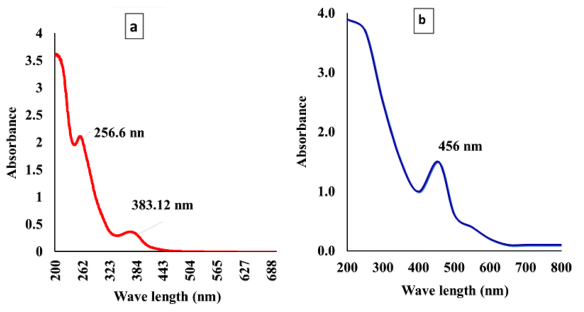
The rapid emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has created a pressing need for innovative and sustainable antimicrobial agents. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are well-known for their potent antibacterial properties; however, conventional chemical synthesis methods often involve toxic reagents and environmental hazards. In this study, an eco-friendly approach was employed for the green synthesis of AgNPs using Punica granatum (pomegranate) peel extract as a natural reducing and stabilizing agent. The extract, rich in polyphenols, tannins, and flavonoids, effectively reduced silver ions (Ag⁺) to metallic silver nanoparticles. A visible color change from pale yellow to dark brown confirmed the formation of AgNPs, and UV–Vis spectroscopy revealed a characteristic surface plasmon resonance peak at ~430 nm. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) indicated the presence of bioactive functional groups responsible for the reduction and capping of nanoparticles. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) confirmed the crystalline nature of the synthesized AgNPs, and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) showed predominantly spherical particles with sizes ranging from 20–80 nm. The antibacterial efficacy of the green-synthesized AgNPs was evaluated against Escherichia coli (Gram-negative) and Staphylococcus aureus (Gram-positive) using the agar well diffusion method. Results demonstrated significant inhibition zones, confirming the strong antimicrobial potential of AgNPs, particularly against S. aureus. The study highlights the dual benefit of utilizing agro-waste for nanoparticle synthesis while producing biocompatible and eco-safe antibacterial agents. These green AgNPs hold promising applications in medical textiles, wound dressings, and water purification systems.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Qurrat Ul Ain Leghari, Muhammad Asad, Ijaz Ahmad, Muhammad Waqas, Shehla Begum, Khan Niaz Khan , Faran Durrani, Madiha Safi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






