A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MOSQUITO BREEDING SITES WITHIN AND AROUND THE COLLEGE ENVIRONMENT: A CASE STUDY OF SULTAN ABDULRAHMAN COLLEGE OF HEALTH TECHNOLOGY, GWADABAWA, SOKOTO STATE, NIGERIA
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr595Keywords:
Mosquito breeding sites , Vector-borne diseases , Environmental sanitation , Public health , Malaria control , Waste disposal , Water storage , Larval source management , Health education , Sultan Abdulrahman College of Health TechnologyAbstract
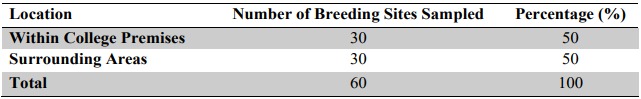
Mosquitoes remain a major public health concern globally, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa where mosquito-borne diseases such as malaria continue to contribute significantly to morbidity and mortality. This study aimed to conduct a comparative assessment of mosquito breeding sites within and around the premises of Sultan Abdulrahman College of Health Technology, Gwadabawa, and Sokoto State, Nigeria. The objective was to identify the types, distribution, and prevalence of mosquito breeding habitats and assess environmental and human-related factors that encourage their proliferation. A cross-sectional descriptive study design was adopted, using observational checklists and environmental assessment tools. Data were collected from stagnant water bodies, uncovered containers, blocked drainages, and bushy surroundings both within and outside the college premises. Findings revealed a higher prevalence of potential breeding sites around the college environment than within, attributed to poor waste disposal practices, lack of drainage systems, and uncovered water storage containers. The study also found that students and residents had limited awareness regarding the control of mosquito habitats. It concludes that intensified public health education, environmental sanitation, and enforcement of hygiene practices are critical to reducing mosquito breeding and, by extension, the incidence of vector-borne diseases. The study recommends regular inspection and larval source management within and around educational institutions.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mubarak Musa Bodinga , Murtala Malami , Marwana Magaji , Mukhtar Salihu Sifawa , Lawal Ibrahim Bodinga (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






