The Impact of Climate Change on Vector-Borne Diseases: A Public Health Perspective
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr382Keywords:
Pesticide safety, environmental pollution, soil fauna, pesticide regulation, pesticide marketAbstract
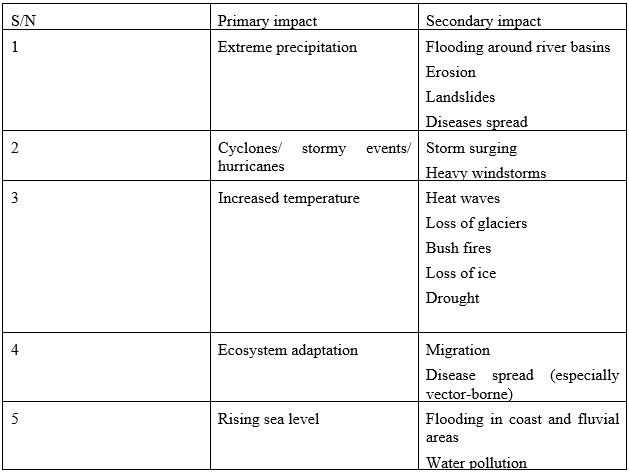
Climate change has significant impacts on human health, particularly on vector-borne diseases (VBDs). VBDs, such as malaria, dengue fever, and yellow fever, are transmitted by vectors like mosquitoes, ticks, and flies. Climate change affects the distribution, behavior, and ecology of these vectors, leading to changes in disease transmission patterns. This paper reviews the impact of climate change on VBDs from a public health perspective. It discusses how climate change affects the transmission of VBDs, including changes in temperature, precipitation, and humidity. The paper also explores how human behaviors, such as migration, urbanization, and land use changes, contribute to the spread of VBDs. The authors highlight the need for integrated approaches to mitigate the impacts of climate change on VBDs. These approaches include vector control measures, such as insecticide-treated bed nets and indoor residual spraying, as well as public health interventions, such as vaccination and disease surveillance. The paper concludes that climate change poses significant challenges to public health, particularly in regions with limited resources and infrastructure. It emphasizes the need for urgent action to address the impacts of climate change on VBDs and to protect human health.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fatima Zahra Abubakar-Otaru, Yusuf Yahaya Miya, Ummu Tukur (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






