PRENATAL AND POSTNATAL ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF MYELOMENINGOCELE TO PREDICT POST-SURGICAL OUTCOMES
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr533Keywords:
Myelomeningocele, prenatal ultrasound, postnatal ultrasound, ventriculomegaly, Chiari II malformation, surgical outcome, neonatesAbstract
Background:
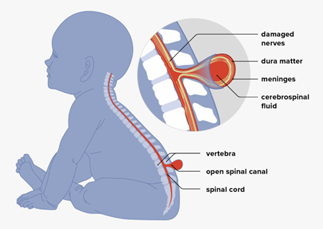
Myelomeningocele (MMC) is a severe neural tube defect associated with significant morbidity, including motor deficits and hydrocephalus. Early diagnosis and surgical intervention are crucial to improving outcomes.
Objective:
To evaluate the prenatal and postnatal ultrasonographic features of myelomeningocele to predict post-surgical outcomes.
Methods:
A prospective observational study was conducted on 20 pregnant women in their third trimester with fetal MMC confirmed between T1 and S1 levels. Prenatal and postnatal ultrasound evaluations were performed to assess lesion characteristics, associated anomalies (e.g., Chiari II malformation, ventriculomegaly), and surgical outcomes. Statistical analysis included descriptive measures and independent t-tests.
Results:
Forty percent of neonates underwent surgery within 24 hours, while 85% experienced at least one post-surgical complication. VP shunts were required in 40% of cases, and 40% of neonates remained wheelchair dependent. A statistically significant association was found between family history and larger lesion circumference (p = 0.000). Only 25% of patients achieved independent ambulation, and 70% required NICU admission.
Conclusion:
Ultrasonography is a valuable diagnostic and prognostic tool for MMC, aiding early detection and guiding surgical planning. Timely intervention and multidisciplinary follow-up remain essential to improving neonatal outcomes, particularly in low-resource settings.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Maria Hameed, Fahmida Ansari, Zaufishan Ahmad, Bibi Naseem (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






