EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA WITH ULTRASOUND AND ITS CORRELATION WITH OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DIABETES
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr233Keywords:
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, BMI, Ultrasound, ObesityAbstract
Background: Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland, a condition that significantly impacts the quality of life in aging men. Ultrasound imaging has emerged as a cornerstone in the assessment of BPH.
Objective: The objective of this study is to evaluate benign prostatic hyperplasia with ultrasound and its correlation with obesity, hypertension, and diabetes.
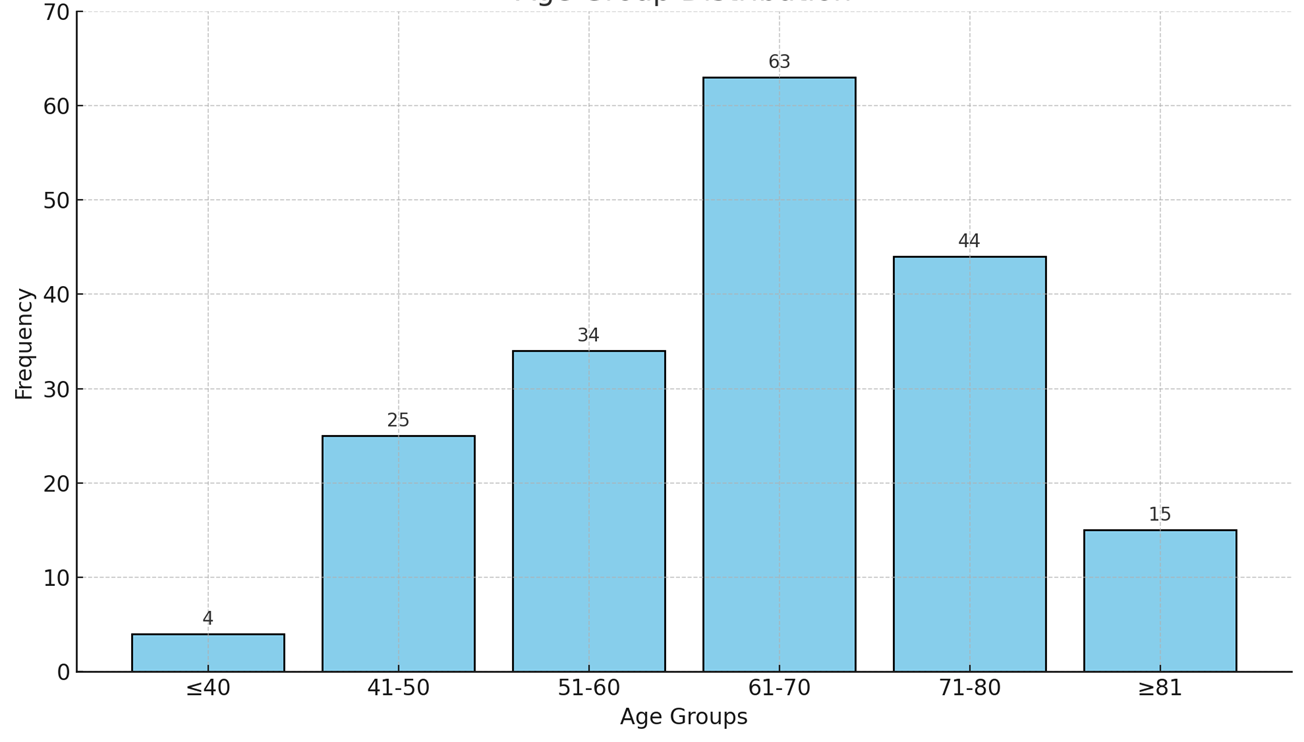
Methodology: Prospective Observational study was conducted in Lahore with convenient sampling technique, 185 males were participated in six-month study. Male who was 30 years above with no history of prostate cancer and surgery were included in study. BMI, Lab tests and Ultrasound scan were performed. To measure the correlation of obesity, diabetes and hypertension with BPH.
Results: The study evaluated 185 male participants (mean age: 65.01 years) prostate weight showing significant correlations with length (r = 0.8540) and width (r = 0.6703). Age demonstrated a moderate positive correlation with prostate weight (r = 0.4626), while BMI showed minimal associations.
Conclusion: Research data confirms the relationship between BPH and conditions like BMI, diabetes and hypertension. It highlights the importance of treating these issues together and using ultrasound as a key tool for better diagnosis and management.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Siraj Ali, Madiha Naheed , Shahzeb, Kalim Ullah, Bilal Ahamd, Abdur Rehman Khokhar (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






