INTEGRATIVE ROLE OF HERBAL BIOACTIVES AND DIETARY MODULATION OF GUT MICROBIOTA IN THE PREVENTION OF GASTROINTESTINAL CANCERS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr580Keywords:
Herbal Medicine, Gut Microbiota, Gastrointestinal Cancer, Polyphenols, Colon Cancer, Prebiotics, Phytochemicals, Dysbiosis, Inflammation, Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)Abstract
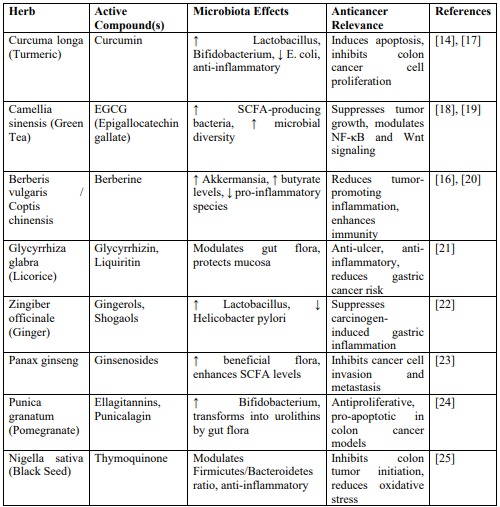
The gut microbiota has emerged as a crucial player in the maintenance of gastrointestinal health and the prevention of various chronic diseases, including cancers of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. A balanced and diverse microbial ecosystem not only facilitates digestion and nutrient absorption but also modulates immune responses and suppresses pro-carcinogenic pathways. Dysbiosis, an imbalance in the composition of gut microbiota, has been increasingly associated with the pathogenesis of colon and gastric cancers through mechanisms such as inflammation, DNA damage, and altered bile acid metabolism. Herbal medicine, rooted in centuries-old traditional healing systems, has recently garnered scientific interest as a promising strategy for restoring gut microbial homeostasis and mitigating cancer risk. Various herbal extracts and phytochemicals possess prebiotic properties, exhibit antimicrobial effects against pathogenic strains, and influence key signaling pathways involved in tumor development. Polyphenol-rich botanicals such as turmeric, green tea, licorice, and berberine-containing herbs have demonstrated the ability to enhance microbial diversity and promote the production of beneficial metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). This review explores the current evidence on the interaction between medicinal plants and gut microbiota, the mechanisms through which these interactions may modulate cancer risk, and recent in vivo and clinical studies supporting their potential. The paper also discusses limitations in current research, the need for personalized microbiota-based therapies, and future perspectives in this evolving field. Understanding how herbal compounds reshape the gut ecosystem opens new avenues for non-invasive, adjunctive cancer prevention strategies rooted in natural medicine.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Akhlaq, Syed Muhammad Kazim Abbas Shah, Muhammad Akram, Muhammad Khaleeq Alum, Syed Rizwan Ali, Hamda Tanzeem Khan (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






