CAMPYLOBACTER JEJUNI AND INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE: CURRENT INSIGHTS AND NANOPARTICLE-BASED INTERVENTIONS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr576Keywords:
Campylobacter jejuni, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, nanoparticles, drug delivery, biofilms, gastrointestinal inflammation, antimicrobial therapyAbstract
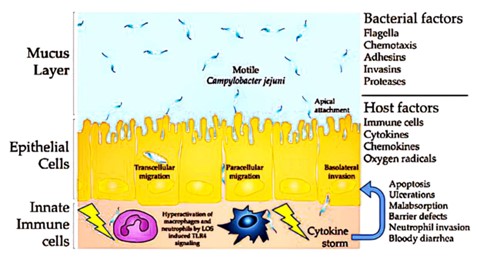
Background: Campylobacter jejuni is one of the major causes of bacterial food poisoning across the globe and recent studies have associated it with worsening of IBD. The fact that IBD is a chronic inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract worsens with infections from enteric pathogens such as C. jejuni in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These effects could be countered through nanoparticle-based therapies that have appeared as a more effective treatment strategy in recent years.
Objective: This review will endeavour to identify current knowledge on the pathophysiological link between C. jejuni and IBD and also assess the viability of nanoparticle-based treatments in moderating this connection.
Methods: The literature from the period 2010 up to 2024 was reviewed systematically, with emphasis on the part played by C. jejuni in IBD and the use of nanoparticle-based therapies. Information was collected from in vitro and in vivo studies, and clinical trials for evaluating the effectiveness of these interventions.
Results: C. jejuni impairs the intestinal barrier, triggers strong inflammation and dysregulates the composition of the gut microbiota in IBD. In preclinical studies, the nanoparticle-based interventions showed promising approaches to decreasing bacterial burden, inflammation, and enhancing mucosal barrier.
Conclusion: Nanoparticles can be used to deliver drugs to C. jejuni infected IBD in a controlled manner and reduce the side effects that are usually associated with the conventional drugs and therapies. But this calls for further research in a bid to harmonize these therapies as well as ascertain their safety in the clinical practice.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fatima Aftab, Aroosh Shabbir, Iqra Safdar, Aysha Noor, Maira Naveed, Asfand Yar Mujahid, Arslan Shuja, Muhammad Mudassar (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






