ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON WATER RESOURCES IN SEMI-ARID REGIONS: A CASE STUDY FROM PAKISTAN
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr512Keywords:
Climate Change, Water Resources, Semi-Arid Regions, Pakistan, Indus Basin, Groundwater Depletion, Hydrological Modeling, Agricultural Impacts, Drought, Water Quality, Climate Adaptation, SWAT Model, Water GovernanceAbstract
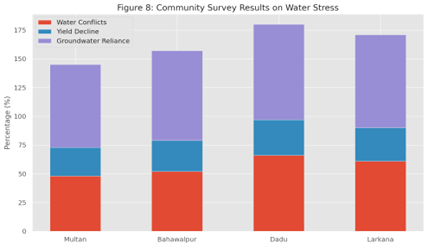
The impact of climate change is posing more and more pressure on water resources in the semi-arid areas where climatic variability directly influences water availability, agricultural productivity and rural livelihoods. In this research paper, the regional impacts of climate change on hydrological and socio-economic aspects of water resources within the semi-arid areas of Pakistan will be studied with reference to certain Indus basin districts. The study utilized mixed methods, including the analysis of long-term climatic and hydrological data (19802024), hydrological modeling using SWAT, water quality of the groundwater, and household surveys that were carried out over the research areas Multan, Bahawalpur, Dadu, and Larkana. The findings further show that annual rainfall decreased by 14.7 percent and the river discharge by more than 20 percent and the average rate of ground water table decline was up to 2.0 meters per year. Water quality, also, has been cracking with concentrations of nitrate and salinity surpassing WHO safety limits in some districts in the groundwater. These water pressures have contributed to severe declines in agricultural output--especially wheat, cotton, and rice--and a rise in costs of irrigation. The community surveys found that the use of groundwater was increasing and the water wars were becoming more prevalent, especially in the drought vulnerable regions. This article highlights the critical necessity of harmonious overall management of water, control of groundwater, eco friendly agriculture, and immediate calamity screening to improve regional water security and the restorative capacity of communities. The results add to the evidence base of Pakistani national climate adaptation policy and provide practical implications of sustainable water management in semi-arid areas across the globe.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Aftab Ahmad Sheikh, Rohul Amin, Mariam Sattar, Aftab Ahmad Khan, Sanober Gul, Muhammad Ibrar Ahmad (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






