INDUSTRY 5.0 AND HUMAN–TECHNOLOGY COLLABORATION: THE ROLE OF AI AND MACHINE LEARNING IN SHAPING FUTURE WORKPLACES
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr617Keywords:
Adaptability, Artificial intelligence, Collaboration, Industry 5.0, Machine learning, Workplace efficiencyAbstract
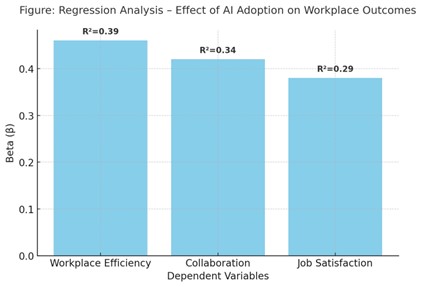
As Industry 5.0 evolved rapidly, it highlighted human technology collaboration, the role of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in shaping future workplaces. The use of AI and ML assist in increasing the efficiency of an organization, employee satisfaction, and team dynamics. It also tackles the issues of transparency, trust, and governance. The goal was to see how the frameworks Industry 5.0 fused human values and technological innovations to reshape workspaces. A mixed-methods approach was adopted. Surveys measuring efficiency, adaptability, and job satisfaction were employed to collect quantitative data while semi-structured interviews of employees and managers in technology driven sectors were conducted to gather qualitative data. Statistical studies show that artificial intelligence adoption has a significantly positive impact on workplace efficiency, adaptability and even job satisfaction. The qualitative findings echoed these results; employees appreciated AI for streamlining tasks but were worried about trust, over-reliance and surveillance. The results suggest that AI and machine learning were not used merely as tools, but as partners in transformation. Nonetheless, the sustainable success of these technology tools depends on ensuring transparent governance frameworks, systematic training of employees and ethical safeguards to mitigate risks of bias and inequality. As per the findings of the research, it was concluded that the concept of Industry 5.0 should be viewed as a socio-technical transformation. Thus, enhancing the relationship between human creative and emotional intelligence with technological innovation. Future studies can look into how AI adoption affects mental health. It can also include interdisciplinary studies and longitudinal studies.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Maria Nafees, Amjad Jumani, Zoobia Rana, Hafiz Muhammad Asad Mustafa, Touqeer Ali Rind, Muhammad Rizwan Tahir (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






