REAL-TIME GENDER AND EMOTION RECOGNITION USING OPTIMIZED DUAL-PATH CNN ARCHITECTURE FOR ENHANCED HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr380Keywords:
Gender Recognition, Face Detection, Feature Extraction, Facial Expressions, Deep Learning, CNNs, Viola-Jones, HCIAbstract
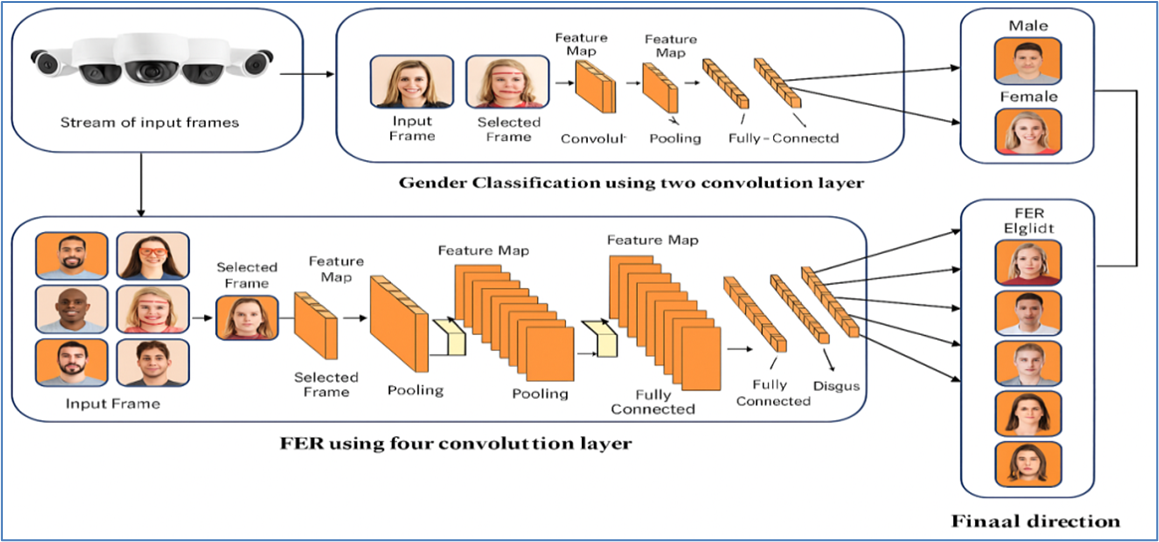
The analysis of facial expressions plays a fundamental role throughout human-computer interaction together with affective computing along with behavioral sciences thereby enabling security surveillance devices as well as healthcare diagnostic systems and smart interactive programs. A research project uses optimized deep learning methods to solve ongoing real-time gender and emotion recognition difficulties stemming from facial expression diversity together with illumination fluctuations and dataset preference. Our proposed framework includes two essential CNN components: (1) a simplified two-layer CNN system for male/female classification and (2) a hierarchical four-layer CNN model for identifying happy and sad expressions together with angry face and other emotions depicted in fear, disgust, surprise and neutral. The proposed framework implements three main technical advancements that include Viola-Jones face detection and optimized convolutional layers with ReLU activation and batch normalization for efficient feature extraction and strategic max-pooling for dimensionality reduction. Performance assessments across benchmark collections including FER-2013, CK+, KDEF, and IMDB indicated 94% success in gender detection and 93% accomplishment in emotional identification, together with real-time implementation capabilities. In controlled environments, the system maintains strong performance yet displays confusion between emotionally related categories of disgust and fear. The research incorporates three main elements to advance the work: (1) a CNN architecture design optimized for precision and speed balance, (2) combined batch normalization and dropout regularization methods to improve feature extraction, and (3) thorough multiple dataset testing to verify generalized performance. The latest networks create fundamental frameworks for future applications in intelligent surveillance and affective robotics as well as behavioral analytics; yet more research needs attention mechanisms that enhance emotion recognition precision during fine-grained emotion differentiation.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Muhammad Qasim Khan, Fazal Malik, Afsheen Khalid, Dilawar Khan, Ashraf Ullah, Rahmat Hussain, Muhammad Javed (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






