IMPROVING COVID-19 INFORMATION RETRIEVAL BY INTEGRATING SEMANTICS AND CLUSTERING
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr236Keywords:
semantic clustering, K-Mean clustering, semantic similarity, COVID-19 ontology, semantic information retrievalAbstract
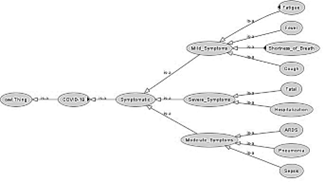
A semantic and natural language processing-based information retrieval system can be very supportive of society and experts in fighting the viral disease pandemic, such as COVID-19. Various emerging technologies, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, the semantic web, and big data analytics, are being progressively applied in information retrieval systems to support data retrieval across different disciplines. The healthcare discipline, especially, requires such systems, applications, and technological support to improve the study and quality of research on the chronic viral disease COVID-19. Wisely arranged and precisely retrieved data in healthcare systems is very helpful in providing quality services and making effective decisions to deal with the COVID-19 pandemic. An information retrieval system can be made more effective in producing more precise results by adding semantics such as semantic textual similarity measures, clustering, and the support of ontology. This research presents an improved information retrieval system by integrating semantic clustering and domain ontology. The K-Means is the most used algorithm in various research schemes for clustering terms, but has shortcomings in the context of computing the similarity or close relationship between concepts. The use of semantic similarity measures between data items in the K-Mean clustering procedure provides an effective method for forming more accurate clusters semantically. Further, the integration of the COVID-19 dataset ontology supports computing the relationship between data items more accurately when forming clusters. The semantic clustering and ontology integration can generate more accurate clusters than the clusters formed only through distance calculation between data items. The results of this research proved a higher accuracy level of results retrieved by information retrieval process.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Shama Zahra , Muskan Fatima , Aisha Hamid , Hafiza Sarwat Noor , Muhammad Zain , Iftikhar Ahmed, Aqsa Khalid , Zeenat Mahmood , Sumaira Younus , Syed Hamza Abbas , Haseeb Nisar , Shama Abid, Yumna Hidayat (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






