OCEAN ACIDIFICATION AND DEGRADATION OF CORAL REEFS: MONITORING OF THE INDICATORS AND INTERVENTIONS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr217Keywords:
Ocean Acidification, Coral Reef Degradation, Environmental Indicators, Climate Change, Marine Ecosystems, Biodiversity Loss, pH Levels, CO₂ Emissions, Coral Resilience, Global CooperationAbstract
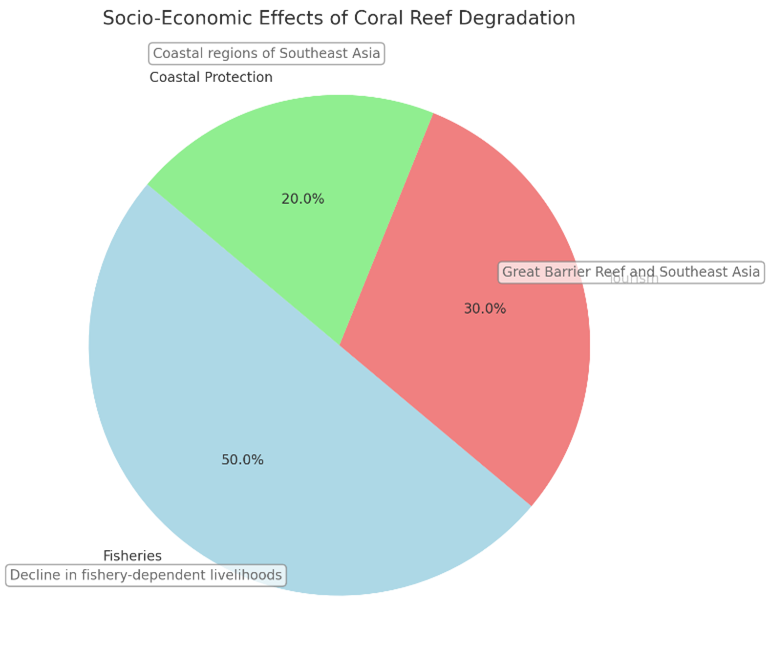
The most influential impact factor in marine ecosystems, especially coral reefs, is ocean acidification caused by increased atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO₂). This article elaborates on the critical link between ocean acidification and degradation of coral reefs, putting emphasis on the monitoring of those environmental indicators and targeted interventions. Coral reefs are the most important elements of biodiversity and coastal protection; they are deteriorating fast under current changes in ocean chemistry, reducing their ability to maintain calcium carbonate structures. The paper examines the main causes and implications of acidification, special consideration is given to the effects on marine organisms such as coral polyps, shellfish, and fish populations. Some of the indicators used to comprehend the process and extent of degradation in coral reefs are water pH, concentration of carbonate ions, and change in temperature. Regional hotspots that are experiencing impacts include the Great Barrier Reef and Southeast Asia, where acidification is more pronounced. The crisis is resulting in the consideration of innovative interventions to reduce damage and improve the resilience of corals. These include practices such as coral gardening, selective breeding for acidification-resistant species, and carbon sequestration as ways to curb CO₂ emission. The paper also further describes policy framework and global co-operation in mitigating the core reasons for ocean acidification. Therefore, the objective of this paper is to provide an integrated scientific awareness, technological application, and grass root approach towards coral reef degradation management. These are some of the critical ecosystems that call for urgent action to safeguard marine biodiversity, food security, and global environmental health.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Imdad Ullah, Sawaira Aman, Fawad Yousaf, Arbaz Khan Khattak, Hani Alam (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






