IMPACT OF SOCIO-ECONOMIC STATUS ON SOCIAL BEHAVIOR AMONG HIGHER SECONDARY SCHOOL STUDENTS: A STUDY OF AGGRESSION AND PROSOCIALITY
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.71146/kjmr189Keywords:
Socio-economic status, social behaviour, aggression, prosociality, quantitativeAbstract
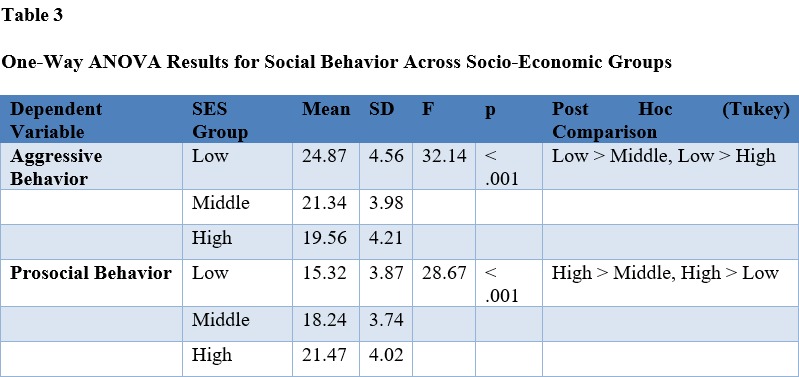
This quantitative study examines the relationship between socio-economic status (SES) and social behaviour, focusing on aggression and prosociality, among higher secondary school students. A stratified random sample of 381 students was selected using Yamane's formula. A self-administered questionnaire with a 5-point Likert scale was employed to collect data. Statistical analysis revealed significant correlations between SES and social behaviour, indicating that students from lower SES backgrounds exhibited higher aggression and lower prosociality. The findings suggest that SES plays a critical role in shaping social behaviour among adolescents. The study's implications highlight the need for targeted interventions to promote positive social behaviour and address the socio-economic disparities in educational settings.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Muzamil Hussain Al Hussaini, Dr Muhammad Shah, Dr Maryam Gul (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.






